Tinderbox Meetup 16JUN25 (Video): AI in Healthcare with Andy Bland—Transforming Medical Knowledge Management
| Level | Intermediate |
| Published Date | 6/16/25 |
| Type | Meetup |
| Tags | AI hallucinations, AI prompting, API integration, Apple Watch, ChatGPT, Claude, Cloud Cannon, Curio, DevonThink, Gemini, GitHub, HTML generation, Hugo, MCP Server, Markdown, Obsidian, Perplexity, Python, RAG (Retrieval Augmented Generation), Scrivener, Tinderbox, Ulysses, clinical decision support, confidence analysis, data analytics, data visualization, electronic health records (EHR), health data collection, knowledge management, local LLMs, medical education, medical literature review, medical research acceleration, medical textbook generation, notebook LM, nudging theory, patient data anonymization, predictive modeling, simulation training, system flow diagrams, token limits, wearable devices, 5CKM, 5Cs of Knowledge Management, Eastgate, Identity Praxis, Inc., Mark Berstein, Michael Becker, Tinderbox |
| Video Length | 01:25:44 |
| Video URL | https://youtu.be/KkAfC--OVPw |
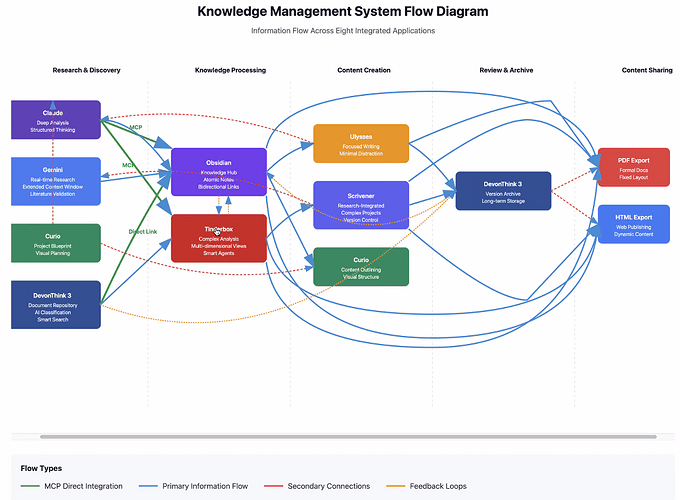
| Example File | km-flow-diagram.html.zip (5.0 KB) |
| Chat | TBX Meetup 15JUN25Chat.txt (8.9 KB) |
| TBX Version | 10 |
| Host | Michael Becker |
This was a tour-de-force meet-up. In this Tinderbox meetup, Dr. Andy Bland (@acbmd), a physician (kidney specialist) and AI enthusiast, shared his innovative approach to using AI models like Claude, Perlexity, and Gemini in his medical practice and knowledge management efforts. He demonstrated how he leverages multiple AI models to accelerate his learning, to review complex medical literature, and to create educational resources. Andy emphasized the need for an AI user to create detailed prompts and to challenge AI’s response ty asking it to perform a confidence analysis and matrix on references and related facts. Andy showcased his work developing an MCP server to integrate AI with tools like Obsidian and Tinderbox, highlighting the potential of AI as a force multiplier in healthcare, not to replace physicians, but to augment their expertise by providing rapid research assistance, generating educational content, and potentially improving predictive modeling. In this discussion, we also explored the challenges of data integrity, privacy concerns, and the future of AI in medical education and patient care. Andy stressed that AI is a powerful tool when used thoughtfully and with subject matter expertise.
Notable Quotes from Dr. Bland
- 12:56 “Claude and its reasoning model really excels in complex technical issues. It is probably the best medical AI that is not 100% medicine focused.”
- 32:14 “What I view AI as is a very smart, very fast, very young colleague. And so for me, it would be the combination of a first-year resident or a fourth-year medical student.”
- 1:04:03 “AI doesn’t solve all our problems. It’s having people who are AI facile, who are able to actually understand what it is that AI is telling them and why it’s telling them.”
- 46:16 “AI has accelerated my knowledge management and learning, probably not joking, 100 to 1000 fold, depending on the topic.”
- 1:16:47 “If you want data to be reliable, you have to make sure the collection agent is reliable. And so there are monitors that are not FDA certified or validated.”
Definitions
- Token, In AI, particularly in natural language processing (NLP), a token is a basic unit of text the model processes—such as a word, part of a word, or punctuation mark. Models like GPT tokenize text using algorithms (e.g., Byte Pair Encoding) to convert it into numerical input they can understand and compute on
- Input token, An input token is any token included in the text that is fed into the AI model. This includes your prompt, prior conversation history, or system instructions. The number and complexity of input tokens affect processing time, cost, and how much context the model can handle.
- Open token, An open token is an incomplete or partial token the model is in the process of generating during inference. It’s often used in the context of streaming output, where the model begins emitting results before the full response is formed, and the last token may still be evolving.
- Vibe coding, Vibe coding is an informal term used to describe writing code—especially with the assistance of AI—based more on intuition, trial-and-error, or creative feel rather than formal specifications or strict planning. It’s common when prototyping or exploring unfamiliar APIs, often relying on AI suggestions to “guess and check” the way forward.
- Artisanal software, Artisanal software refers to custom-crafted, small-scale software designed with care, intention, and deep attention to detail—often by a single developer or a small team. In the AI era, it contrasts with mass-produced code, favoring elegance, maintainability, and human creativity, sometimes augmented by AI but not dominated by automation.
- Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG), is an AI architecture that combines information retrieval with text generation to improve the relevance and factual accuracy of responses 1) Improves factual accuracyj, 2) Keeps models lightweight, and 3) Enables up-to-date responses. Without RAG: The model relies only on its training data (possibly outdated). With RAG: It retrieves the latest news articles or blog posts and generates a response based on that fresh content.
- 20% of medical practice is based in science.
- GIGO, Garbage In, Garbage Out
- MUMPS (“Massachusetts General Hospital Utility Multi-Programming System”)
- EHR, stands for Electronic Health Record
Resources
-
AI Models
- Claude AI
- ChatGPT
- Gemini
- Perplexity.ai, use for search (pro version will generate spreadsheets)
- DeepSeek’
- NotebookLM
- HuggingFaces
-
AI GUI
-
Other Apps
-
Web creation and hosting
-
Tinderbox Supporting Material
-
Other